Bouffalo ISP Protocol V1: Difference between revisions
| (9 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
It is integrated in [[:Category:BL602_Series|BL602]], [[:Category:BL702_Series|BL702]], [[:Category:BL602_Series|BL808]] and [[:Category:BL602_Series|BL616]] series of chips, although, every series have some improvements to this protocol. | It is integrated in [[:Category:BL602_Series|BL602]], [[:Category:BL702_Series|BL702]], [[:Category:BL602_Series|BL808]] and [[:Category:BL602_Series|BL616]] series of chips, although, every series have some improvements to this protocol. | ||
= List of supported interfaces per chip = | |||
List of available interfaces for specific chips: | List of available interfaces for specific chips: | ||
| Line 12: | Line 14: | ||
! SDIO | ! SDIO | ||
! JTAG | ! JTAG | ||
! SD Card | |||
|- | |- | ||
| BL602 Series | | BL602 Series | ||
| Yes | | Yes | ||
| | | No | ||
| Yes | | Yes | ||
| ? | | ? | ||
| No | |||
|- | |- | ||
| BL702 Series | | BL702 Series | ||
| Line 24: | Line 28: | ||
| No | | No | ||
| ? | | ? | ||
| No | |||
|- | |- | ||
| BL808C | | BL808C | ||
| Line 30: | Line 35: | ||
| ? | | ? | ||
| ? | | ? | ||
| Broken? | |||
|- | |- | ||
| BL808D | | BL808D | ||
| Line 36: | Line 42: | ||
| ? | | ? | ||
| ? | | ? | ||
| N/A | |||
|- | |- | ||
| BL606P | | BL606P | ||
| Line 42: | Line 49: | ||
| ? | | ? | ||
| ? | | ? | ||
| N/A | |||
|- | |- | ||
| BL616 Series | | BL616 Series | ||
| Yes | | Yes | ||
| Yes | | Yes | ||
| ? | |||
| ? | | ? | ||
| ? | | ? | ||
| Line 52: | Line 61: | ||
= Getting into ISP/BootROM mode = | = Getting into ISP/BootROM mode = | ||
Currently the BootROM is not explored enough, to know how exactly the boot process works within it, although, we | {{Fmbox | ||
| type = system | |||
| text = Currently the BootROM is not explored enough, to know how exactly the boot process works within it, although, we will describe here already known and tested boot flows. | |||
}} | |||
Currently, there are two ways of getting into ISP mode, which we will describe in following sections: | |||
| | == Via GPIO == | ||
Every chip using ISP Protocol V1 have ability to get into ISP mode by specifying voltage level on specific pin during boot time. This mechanism is implemented within BootROM code. | |||
| | |||
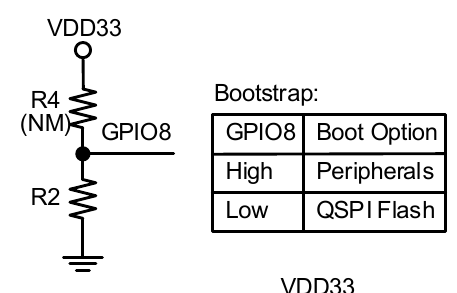
| | BL602 as example, the boot pin needs to be pulled to it's according level (most of times HIGH) 0.1s before powering up the chip via PU_CHIP, and then boot pin needs to be kept at specified level at least 2ms after PU_CHIP get HIGH. | ||
| | |||
| | {{Collapse top|title=Example hardware layout|width=unset}} | ||
| | Example is taken from BL602 Datasheet | ||
| | |||
| | [[File:Bl602_bootpin_layout.png]] | ||
| | {{Collapse bottom}} | ||
| | |||
{| class="wikitable" | |||
|- | |||
! Chip | |||
! Pin | |||
! ISP Mode when pin is | |||
! Note | |||
|- | |||
| BL602 Series | |||
| IO8 | |||
| High | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
| BL702 Series | |||
| IO28 | |||
| High | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
| BL808 Series | |||
| IO39 | |||
| High | |||
| Multiplexed with QSPI D3 pin | |||
|- | |||
| BL616 Series | |||
| IO2 | |||
| High | |||
| Multiplexed with JTAG? (not 100% confirmed) | |||
|} | |||
== Via software == | |||
There are registers to reboot the chip and automatically launch ISP mode. (TODO) | |||
= Handshake = | = Handshake = | ||
= Run firmware = | |||
Latest revision as of 06:19, 3 June 2023
This page describes Bouffalo ISP Protocol V1, which is ISP protocol used to run images, write images to Flash or program fuses via UART, USB, SDIO or JTAG.
It is integrated in BL602, BL702, BL808 and BL616 series of chips, although, every series have some improvements to this protocol.
List of supported interfaces per chip
List of available interfaces for specific chips:
| Chip | UART | USB | SDIO | JTAG | SD Card |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BL602 Series | Yes | No | Yes | ? | No |
| BL702 Series | Yes | Yes | No | ? | No |
| BL808C | Yes | Broken | ? | ? | Broken? |
| BL808D | Yes | N/A | ? | ? | N/A |
| BL606P | Yes | ? | ? | ? | N/A |
| BL616 Series | Yes | Yes | ? | ? | ? |
Getting into ISP/BootROM mode
| Currently the BootROM is not explored enough, to know how exactly the boot process works within it, although, we will describe here already known and tested boot flows. |
Currently, there are two ways of getting into ISP mode, which we will describe in following sections:
Via GPIO
Every chip using ISP Protocol V1 have ability to get into ISP mode by specifying voltage level on specific pin during boot time. This mechanism is implemented within BootROM code.
BL602 as example, the boot pin needs to be pulled to it's according level (most of times HIGH) 0.1s before powering up the chip via PU_CHIP, and then boot pin needs to be kept at specified level at least 2ms after PU_CHIP get HIGH.
| Chip | Pin | ISP Mode when pin is | Note |
|---|---|---|---|
| BL602 Series | IO8 | High | |
| BL702 Series | IO28 | High | |
| BL808 Series | IO39 | High | Multiplexed with QSPI D3 pin |
| BL616 Series | IO2 | High | Multiplexed with JTAG? (not 100% confirmed) |
Via software
There are registers to reboot the chip and automatically launch ISP mode. (TODO)